-
About Us

Dabur India Limited is a leading Indian consumer goods company with interests in Hair Care, Oral Care, Health Care, Skin Care, Home Care and Food & Beverages.
-
Our Brands

Dabur presents a range of Herbal & Ayurvedic Personal Care products, created to make you look and feel good. Bringing together the gentle touch of nature and Ayurveda's wisdom .
-
Investors

Read our recent and archived releases, quarterly results, annual reports and financial statements. Initiatives Investor Centre.
-
Newsroom

Welcome to Dabur Media Centre. In this section, you’ll find our latest Press Releases arranged in a chronological order. The Press Releases have been further
-
Ayurveda & you

Our curated Collection of Ayurvedic knowledge for you. We at Dabur are working towards helping people lead a healthy and balanced life.
-
Sustainability
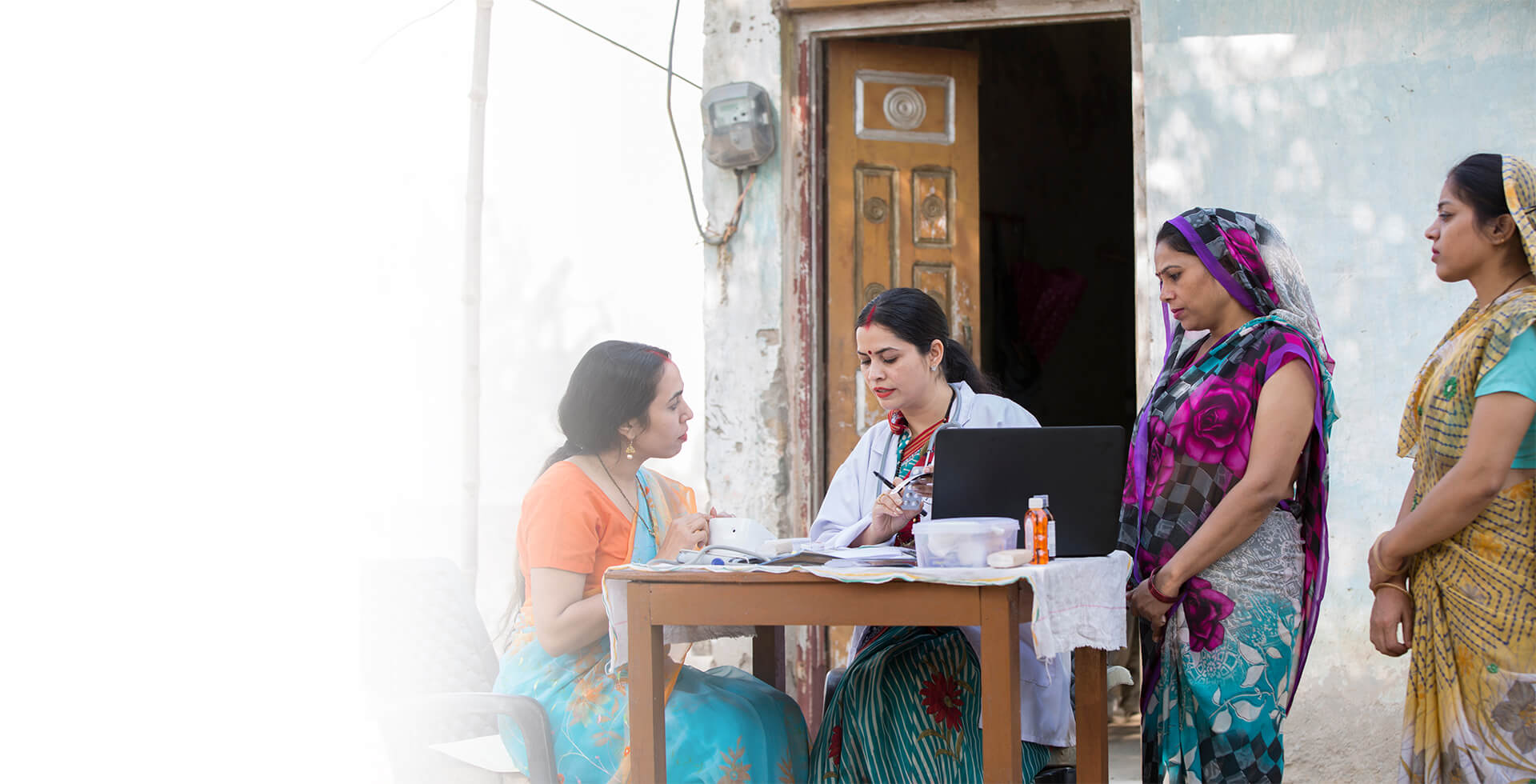
Dabur has been engaged in community development activities since 1994 and is committed to making a positive contribution to the communities where we source, live, work and sell our products.
-
Join Us

At Dabur, we are very passionate about winning and this has been engrained in DNA of the organization.
-
Support
- Home > Ayurveda & you > Ayurveda & Science > Ayurvedic & Medicinal Plants
Ayurveda and Science
Bael/बेल/Aegle marmelos/Bilva/Bengal Quince
AYURVEDIC & MEDICINAL PLANTS
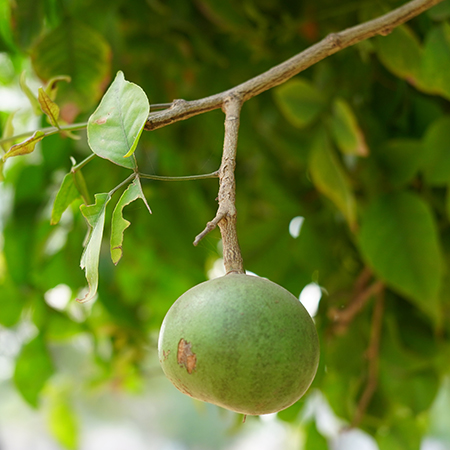

Aegle Marmelos Uses
Bilva has been used extensively in the treatment of dysentery and diabetes as recommended by Indian Ayurveda.
Aegle Marmelos Uses are as follows:
- Aegle Marmelos uses include dried fruit pulp being used in many parts of India in preparation of summer drinks, which helps overcome sunstrokes.
- Bael leaves are used in the preparation of salads.
- Bael fruit pulp absorbs the toxins produced by bacteria and other pathogens in the intestine thus helping in the treatment of dysentery.
- Bael can be used in the formulation of Ayurvedic medicine for loss of appetite.
- Bael extract oil is used to cure respiratory problems.
- Bael fruit is used in the preparation of candy, squash, toffee, pulp powder, and other eatable products.
- Aegle Marmelos is anti-inflammatory in nature. Its extracts when applied on the exposed area, help to cure inflammation
- Aegle Marmelos leaf juice with honey can prove useful for treating fever.
- Aegle Marmelos can be used to treat tuberculosis.
- Aegle Marmelos is rich in anti-oxidants which helps in insulin secretion which leads to low blood sugar levels.
Bark has been reported to have beneficial effects in diabetes.
Chemical Composition
The pulp of the fruit contains mucilage, pectin, sugar, tannic acid and a volatile oil. The wood ash contains potassium and sodium compounds, phosphates of lime and iron, calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, silica etc.
Pacifies kapha and vata.
Read more about various ailments, it's causes, symptoms, ayurvedic treatments, etc.
Know the story behind other medicinal Ayurvedic ingredients

Chitvan
.jpg)
Ghee Kunwar

Ketaki

Mandukaparni


